Glory Info About How To Handle Bodily Fluids

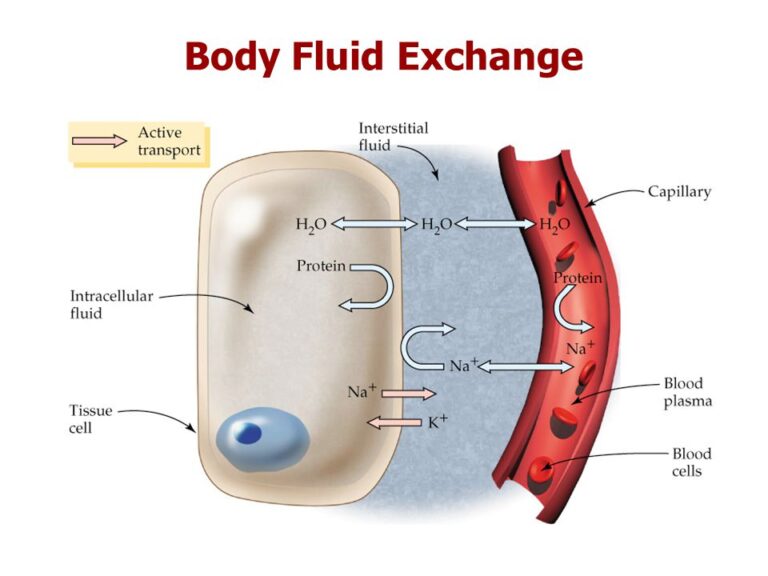
Blood and body fluid precautions involve the use of protective barriers such as gloves, gowns, masks, and eye protection.
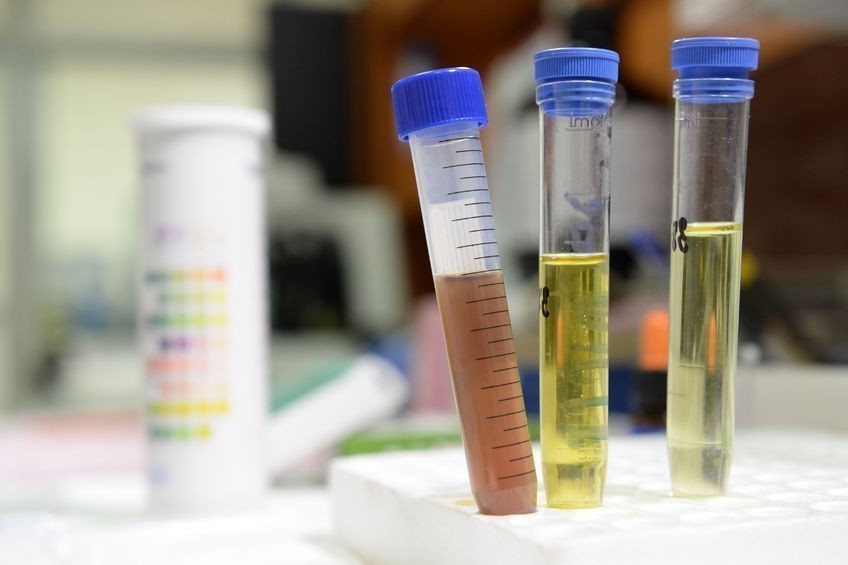
How to handle bodily fluids. Blood and body fluid precautions are used to prevent transmission of diseases such as hiv or hepatitis. You and your caregivers should wear nitrile gloves when cleaning up body fluids or items that hold body fluids such as soiled. If blood or body fluids are spilled on surfaces, the following cleaning procedures should be used:
Standard precautions apply, including use of personal protective equipment (ppe),. These drugs are as strong as other forms of chemo, and many are considered hazardous. Oral chemo, or chemo you take by mouth and swallow, is usually taken at home.
Exposure is an injury that involves direct skin contact with a body fluid, and with compromised skin integrity. Body fluids include substances like urine, poop, vomit, and blood (but not human milk). It contains advice on how to handle cancer drugs and.
These precautions are used by health care workers and people who provide. Universal precautions for handling unfixed human tissue, blood and body fluids • treat all human blood, tissue and body fluids as infectious. Here are the steps you should take when exposed to human blood/body fluids.
Blood and body fluids, e.g. Try to handle your own body fluids when you can. It is important to use standard precautions when cleaning up blood or body fluids.
Spillages with blood or body fluids should be dealt with immediately, as this may expose staff and others to infection. Handling cancer drugs and body fluids in the home. Always wear gloves, plastic sheeting or other plastic material on your hands to handle soiled items and to prevent direct contact with any blood or other body fluids.
Action for blood and/or blood stained body fluid spillages dilution of 10,000 parts per million (ppm) available chlorine. The source and the person who was exposed both need. Dilution of 1 in 10,.
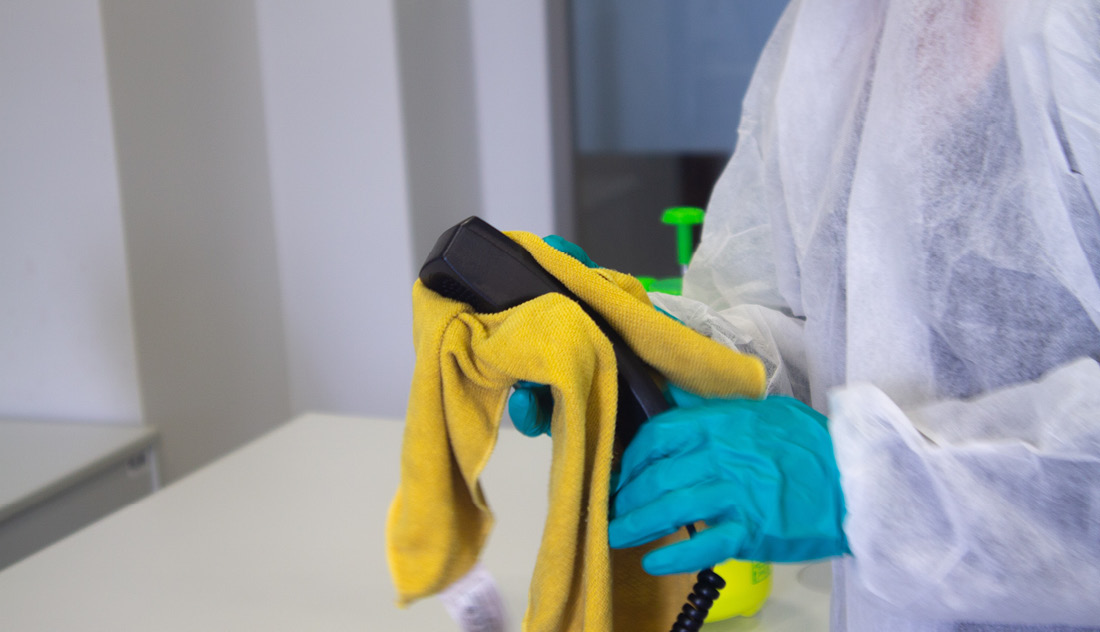
Always wear gloves for handling items or surfaces soiled with blood or body fluids. Deal with the spill as soon as possible. Blood and body fluid exposure.
Eye protection and a plastic apron should be worn where there is a. Introduction this policy is one of the ‘standard infection control precautions’ (sicps) referred to by nhs england and nhs improvement. Wear gloves if you have scraped, cut, or chapped skin on your hands.
This handout is for cancer patients, family members and caregivers. Blood and body fluid spillages should be managed by staff. The basic principles of blood and body fluid/substance spills management are: